

Securing a Cyber Insurance Policy
Cyber insurance is one option that can help protect your business against losses resulting from a cyberattack. For business owners considering cyber insurance, discuss what policy would best fit your company’s needs with your insurance agent.
The following infographics illustrate hypothetical cause-and-effect examples of cyber liability claims. The scenarios described below are completely fictional, but similar circumstances still pose real threats to your business.

The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) recently published guidelines for businesses seeking a suitable cyber policy, the FTC’s list of important coverage points.
These include:
- Access to a 24/7 breach hotline
- Incident response costs, such as computer forensic services, legal counsel and customer notification and call center services
- The cost of recovering or replacing lost or stolen data
- Income loss due to business interruption following a cyber incident
- Cyber extortion and fraud
- Third-party coverage, such as payments to consumers affected by a breach, litigation costs, and losses related to defamation and intellectual property rights infringement
The guidelines provide a good starting point for those businesses in the market for a cyber insurance policy.
Evaluating Your IT System
One way to protect your valuable information is to make sure your IT system is functioning free of vulnerabilities. Getting to know how your system works is a critical first step in preventing a cyberattack. There are free websites you can use to assess your risk, or you can hire an IT analyst to assess your system. Understand your data flow, identifying points of entry and exit for information, and think about who should have access to this information.
It’s important to take inventory of your technology (computers, servers, and printers), documenting their make and model, serial number, and whether they’re connected to the internet.
Next, inventory your software and take note of when the last updates occurred, where backups are stored, and how often you back up information. And inventory your programs and security systems, including ransomware, malware, antivirus software, and firewalls.
Although these efforts may seem tedious, they are vital in protecting important company information, as well as your clients’ private information. It is not necessary for you to become an expert on your IT system, but you should have a working knowledge of it. The more you know and the better you prepare, the safer your business data is.
Read the hypothetical examples in the infographic below for a better understanding of the causes and effects of technology issues that could affect your business in reality.
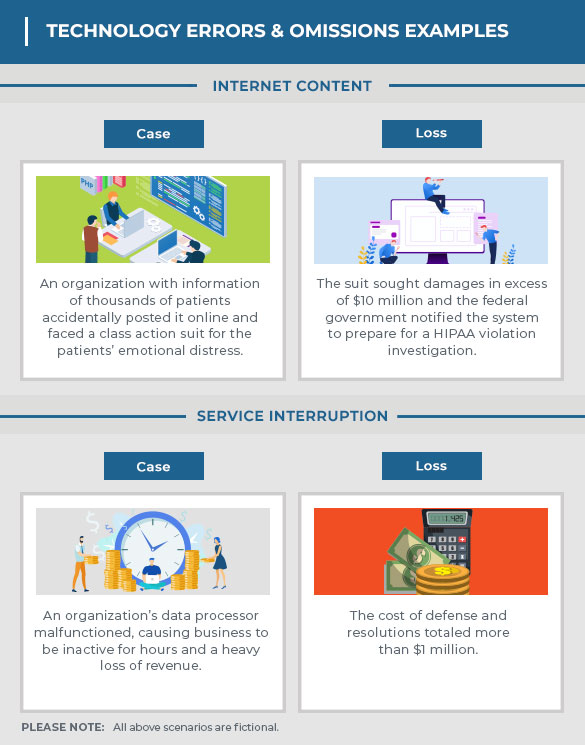
Unfortunately, hackers are unpredictable, which means you never know when they might try to attack. The best defenses are a well-trained staff who can recognize suspicious activity to prevent an attack, and a series of protocols and procedures that can minimize the damage done if a cyberattack occurs. Many businesses think they are not at risk, but they are. Be prepared. Protect your business. You and your clients’ most precious information is at stake.
Establishing Cybersecurity Policies
You can never be certain when and how a hacker will attack your company, but you can take precautionary measures. Most successful cyberattacks happen because an untrained employee opens a phishing email or is duped by a malware or an eavesdropping attack. The best defense, then, is training employees to understand what to look out for and what to do in the event of a cyberattack. Here are some suggestions for company policies to prevent cyberattacks:
- Make sure there is a protocol requiring a passcode or a password system for accessing confidential information
- Regulate employee access to social media on work devices
- Establish guidelines for access to employee email on personal devices, as well as using public Wi-Fi
- Create procedures regarding employee termination to ensure security
- Routinely back up information and store it off-site, so you can still access information if a data breach occurs
Get your hands on our plan.
Ready to get started? Download and print the complete Business Blueprint to keep, read and use as a continued resource.
